- Introduction
-
The Port Division under the Ministry of Ports, Shipping, and Waterways plays a pivotal role in the strategic development, regulation, and modernization of India’s All Major Ports. Presently, there are 14 Major Ports out of which 12 Major Ports are operational. The mandate of the Port Division primarily revolves around the development, modernization, and efficient management of the Major Ports in India to support and enhance the country's maritime trade infrastructure. This includes formulating acts, rules, regulations, policies, and guidelines etc. for port governance, planning and implementing capacity expansion projects, promoting Public-Private Partnerships (PPP), and ensuring seamless and sustainable port operations. The division also focuses on improving port efficiency through digitization, mechanization, and performance monitoring, while integrating green initiatives to align with national sustainability goals. Overall, the Port Division plays a central role in building a robust, competitive, and environmentally responsible port sector.
Formulation of Acts, Rules, and Policy Frameworks
A major key function of the Port Division is the formulation and implementation of legislative and regulatory frameworks that govern port development and administration. The enactment of the Major Port Authorities Act, 2021 marks a significant milestone in this regard. This Act replaces the century-old Major Port Trusts Act, 1963, with a more contemporary governance model that grants greater autonomy to major ports and promotes efficiency, transparency, and ease of doing business. In addition to Acts, the Port Division also develops rules, guidelines, and model concession agreements that streamline the public-private partnership (PPP) model, enabling private sector participation in port operations and infrastructure development. These legal instruments are continuously reviewed and updated to align with global best practices and India's evolving trade requirements.
Performance Enhancement of Major Ports through Monitoring
The Port Division is also play a important role for monitoring the operational efficiency of major ports through a well-defined set of performance indicators. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) such as Average Turnaround Time (TRT), Output per Ship Berth Day (OSBD), Pre-Berth Detention Time, and Port Dwell Time etc. are regularly tracked to assess and improve port productivity and service quality. These metrics help identify bottlenecks, streamline operations, and enhance overall cargo handling efficiency.
Through a multi-faceted approach involving policy reforms, sustainability measures, and data-driven performance management, the Port Division continues to play a critical role in transforming India’s port sector into a modern, efficient, and environmentally responsible system. These initiatives not only support India’s trade competitiveness on the global stage but also contribute to national goals like Aatmanirbhar Bharat and Green India Mission.
Green Initiatives for Sustainable Port Development
In line with the national commitment to climate change mitigation and sustainable development, the Port Division has initiated several green port initiatives. A key milestone is the launch of the Harit Sagar Guidelines, 2023, which provide a comprehensive framework for green port development. These guidelines emphasize environmental sustainability, reduction in carbon emissions, promotion of renewable energy, and ecological protection in all port operations and planning. One of the flagship programmes under this initiative is the Green Tug Transition Programme (GTTP). This programme aims to convert at least 50% of all tugs in major ports into green tugs powered by alternative fuels like electricity, LNG, Green Methanol or green hydrogen by 2030. The goal is to transition all tugs to green energy by 2047, in alignment with India’s broader net-zero targets. This initiative will help reduce the maritime sector’s dependence on fossil fuels and significantly lower emissions in port waters. Furthermore, ports are being encouraged to adopt shore-to-ship power, electrification of cargo handling equipment, rainwater harvesting, and sustainable waste management systems. Renewable Energy (RE) share to be increased to 60 % across all major ports. As global trade patterns evolve and environmental challenges mount, the Port Division remains committed to building resilient and future-ready port infrastructure for the country.
Port Performance Ranking
To promote healthy competition and continual performance improvement among major ports, the Port Division has instituted performance benchmarking mechanisms. The Sagar Aankalan Guidelines were introduced to provide a structured framework for performance monitoring and ranking of ports. These guidelines assess ports across various Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), such as average turnaround time, berth productivity, cargo evacuation speed, dwell time, and more. The port performance rankings are released periodically and are used as a tool to encourage accountability and performance enhancement. They also inform policy decisions and resource allocation. Ports that perform well under this framework are often showcased as models of best practices, and their strategies are replicated at other ports.
- Major Ports & Non-Major Ports
-
There are 14 major ports out of which 12 Major Ports are in Operation and 200 non-major ports (minor ports) in the country. While the Major Ports are under the administrative control of Ministry of Ports, Shipping and Waterways, the non-major ports are under the jurisdiction of respective State Maritime Boards/ State Government. Out of the 200 non-major ports, around 65 ports are handling cargo and the others are “Port Limits” where no cargo is handled and these are used by fishing vessels and by small ferries to carry passengers across the creeks etc
- Major Port Authorities:
-
Jawaharlal Nehru Port Authority
Syama Prasad Mookerjee Port Authority
- Major Port Authority Act, 2021 and Indian Port Act, 2025
-
The Major Port Authorities Act, 2021 provide for regulation, operation and planning of Major Ports in India and vests the administration, control and management of such ports upon the Boards of Major Port Authorities. The legislation empowers these ports to perform with greater efficiency on account of increased autonomy in decision making and by modernizing their institutional framework.
Sr NO. Act Name Link 1 Major Port Authority Act 2021 Download 2 Indian Ports Act, 2025 Download Rules Under Major Port Authority Act, 2021
Sr NO. Guidelines Link I Audit and Accounts Download II Adjudicatory Board Download III Chairperson & Deputy Chairperson Download IV CSR Download V Master Plan and Application Funds Download VI Money in Sinking Fund Download VII Scale of Rates Download - The Adjudicatory Board For Major Ports
-
The Major Port Authorities (MPA) Act, 2021 has come into force with effect from 03 November 2021. With the said Act coming into effect, consequently, the Major Port Trusts (MPT) Act, 1963, stands repealed.
1. With the MPT Act, 1963, repealed, the tariff-setting functions by Tariff Authority for Major Ports (TAMP), stands withdrawn. Section 27 (1) of the MPA Act empowers the Major Ports to determine the tariff for services rendered by them and also for access to port assets including the port land.
2. As per the stipulation given at Sub section (1) of Section 54 of the MPA Act 2021, the Central Government shall constitute an Adjudicatory Board to exercise the jurisdiction, powers and authority conferred on such Adjudicatory Board under Section 32 and Section 58(1) of the MPA Act, 2021. As per Section 55 read with Section 56 of the MPA act, 2021, the Adjudicatory Board shall consist of a Presiding Officer who would be a retired Judge of the Supreme Court of India or a retired Chief Justice of a High Court and 2 Members who would be retired Chief Secretary of a State Government or equivalent; or a retired Secretary of the Government of India or equivalent
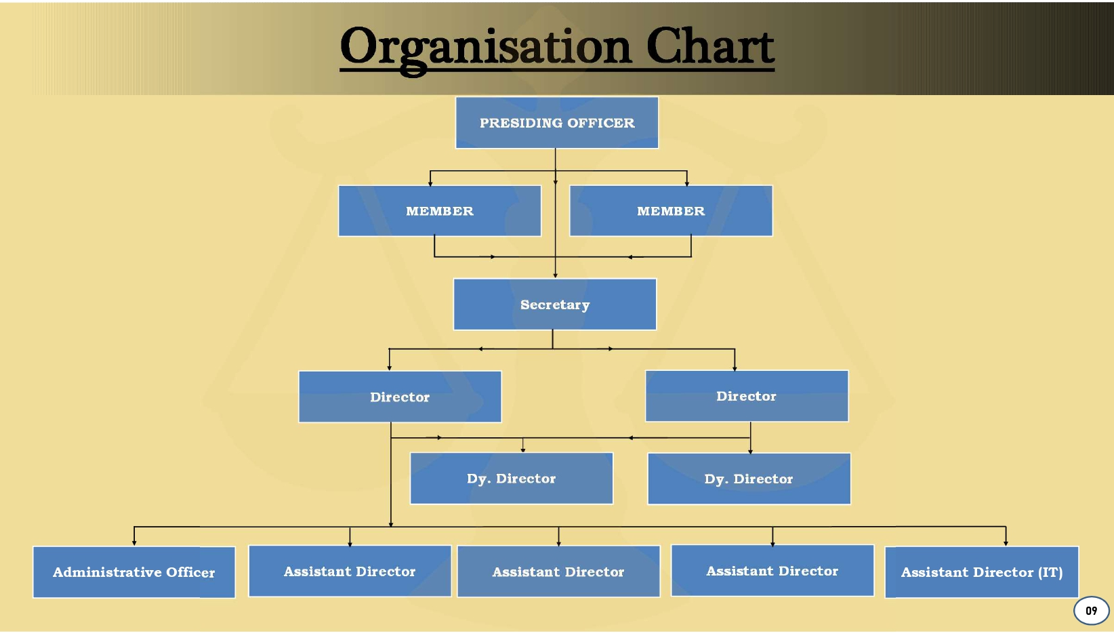
3. In pursuance of Sub-sections (1) and (2) of Section 54 and Section 55 of the said Major Port Authorities Act, 2021, the Central Government has constituted the Adjudicatory Board for Major Ports (ABMP) on 13 August 2025 vide Gazette Notification No.3647 dated 13 August 2025 vide Gazette Notification No.3647, comprising of a Presiding Officer and two Members, as given below-
(i)
Justice Ashish Jitendra Desai
Former Chief Justice, Kerala High Court
- Presiding Officer
(ii)
Shri Chirravuri Viswanath
Former Secretary, Department of Consumer
Affairs, and Former Member, National
Consumer Dispute Redressal Commission (NCDRC)
- Member
(iii)
Dr. Sanjeev Ranjan
Former Secretary, MOPSW, and Technical Member,
NCLT
- Member
4. With the constitution of the ABMP, the constituted under Section 47A of the (erstwhile) Major Port Trusts Act, 1963, TAMP has ceased to exist with effect from 13 August 2025.
5. As per Section 58(1) of the MPA Act 2021, the Adjudicatory Board shall perform the following functions other than tariff setting:
(a). The functions envisaged to be carried out by the erstwhile Tariff Authority for Major Ports arising from the Tariff Guidelines of 2005, 2008, 2013, 2018 and 2019 and tariff orders issued by the said Authority.
(b). To receive and adjudicate reference on any dispute or differences or claims relating to rights and obligations of Major Ports and Public Private Partnership concessionaires or captive users for dedicated berth within the framework of their concession agreements and to pass orders after considering and hearing all the parties involved in the dispute.
(c). To appraise, review the stressed Public Private Partnership projects as referred by the Central Government or the Board, and to suggest measures to revive such projects;
(d). To look into the complaints received from port users against the services and terms of service rendered by the Major Ports or the private operators operating in the Major Ports and to pass necessary orders after hearing the parties concerned; and
(e). To look into any other matter relating to the operations of the Major Port, as may be referred to it by the Central Government or the Board, and to pass orders or give suggestions, as the case may be.
6. The head office of the ABMP is at Mumbai and is operating from the premises of the erstwhile TAMP.
Org Chart
- Guidelines
-
- Guidelines for Establishing a floating Storage Re-gasification Unit (FSRU) at Major Ports
- Guidelines for Treasury Investment Improvement
- Policy for award of Waterfront and Associated Land to Port Dependent Industries in Major Ports
- Land Policy Guidelines
- Berthing Policy
- Harit Sagar - Green Port Guidelines (May 2023)
- Sagar Aankalan Guidelines
- GTTP SOP
- Final CSR guidelines issued on 29 June 23